Key Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Generator Configurations
When choosing a generator for your power needs, it is essential to understand the differences between a three-phase and a single-phase configuration. The distinction between the two significantly impacts various aspects of your operations, including efficiency, cost, and application suitability. In this article, we will analyse the critical differences between single-phase and three-phase configurations to help you make an informed decision when selecting a generator.
What is a Single-Phase Generator?
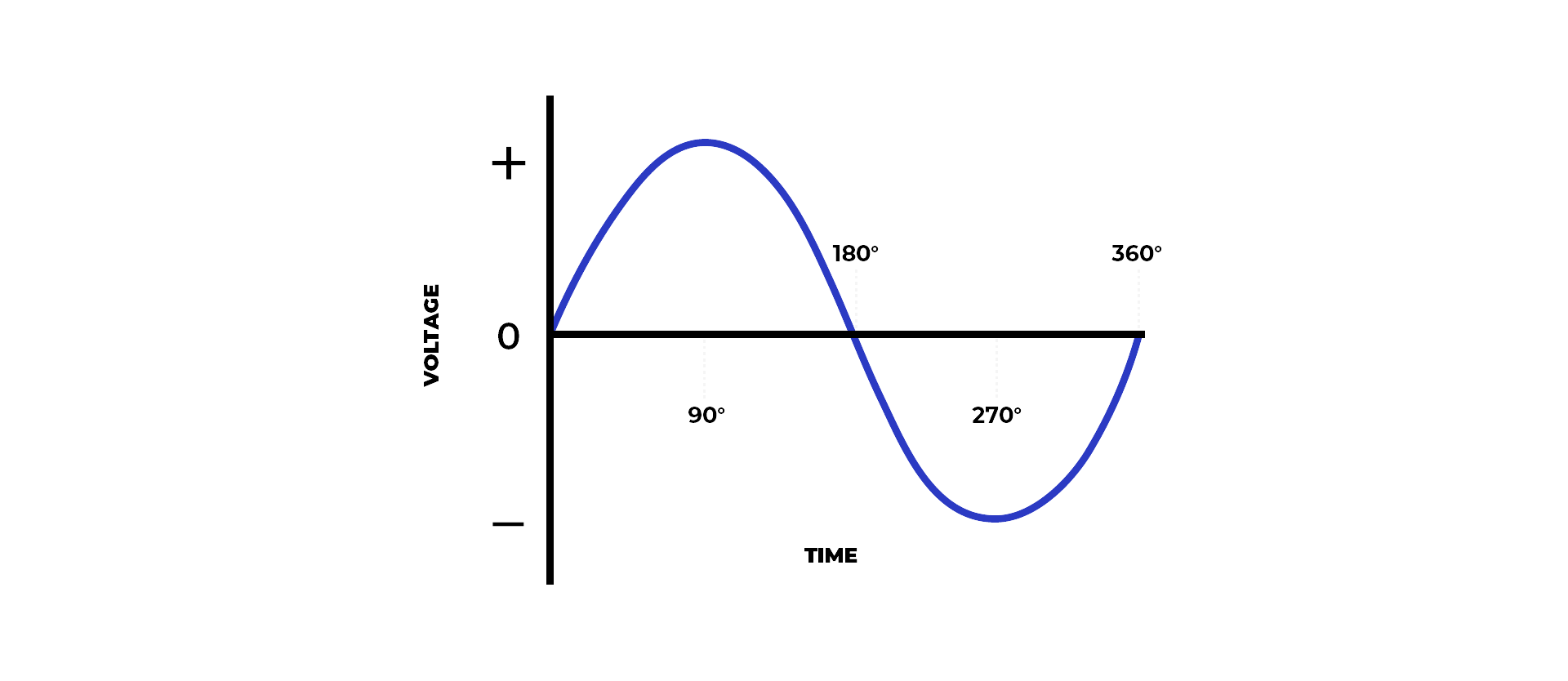 Fig.1 Single-Phase Power
Fig.1 Single-Phase Power
A single-phase generator delivers power in a simple manner, as shown in the graph above, and usually provides power at around 190 volts and 220 volts. This configuration is commonly used in applications with light electrical loads, such as computers, lights, fans, and refrigerators. Because of its simplicity, they are generally smaller than a three-phase generator, making them ideal for smaller-scale operations such as a backup power supply or small commercial/residential operations.
What is a Three-Phase Generator?
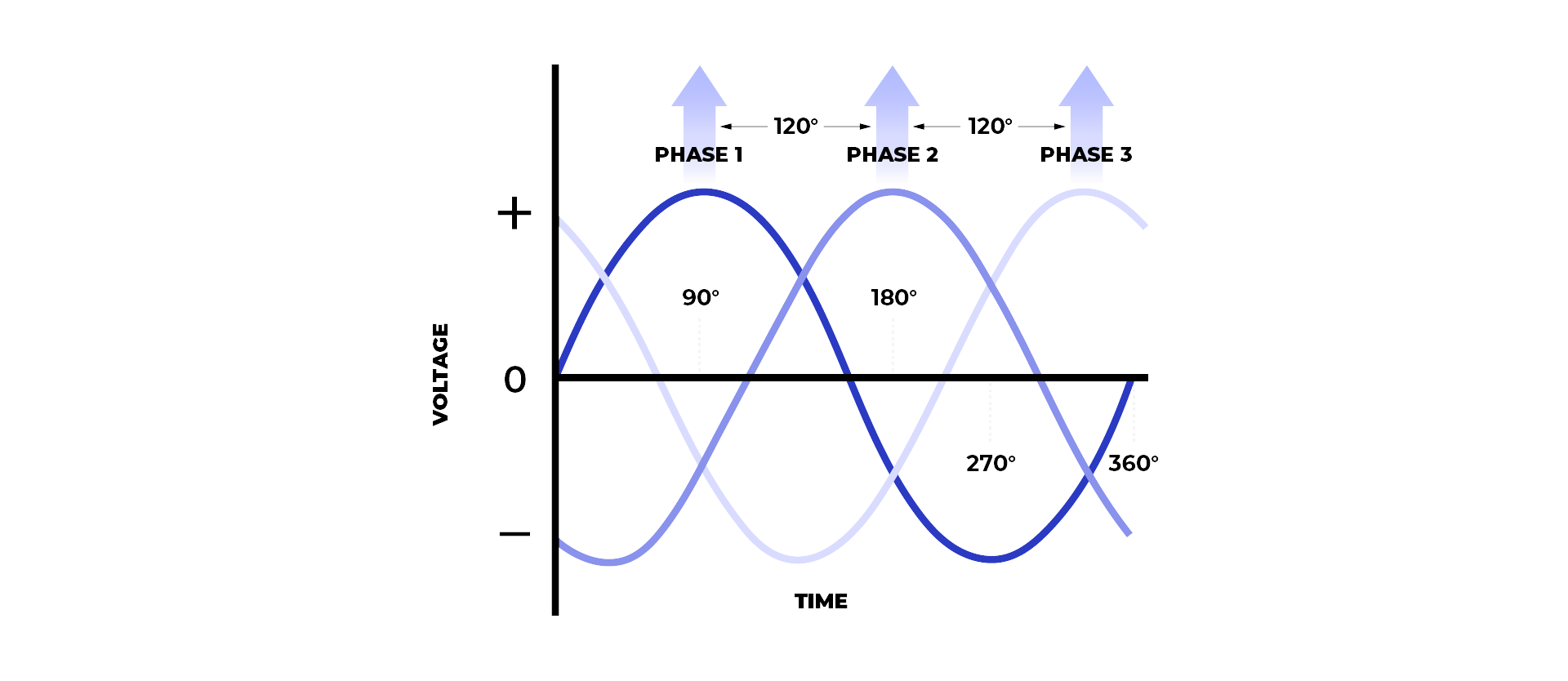 Fig.2 Three-Phase Power
Fig.2 Three-Phase Power
Conversely, a three-phase generator delivers power in a complex manner, as shown in the graph above, and usually provides power at around 380 volts and 440 volts. This configuration is commonly used in high-load equipment such as air compressors, industrial water pumps, and ventilation fans. Due to its stable and constant power flow, a three-phase generator is usually found in heavy industries like agriculture, construction sites, and data centres.
Key Differences between Single and Three-Phase Generator
The main difference between a single and three-phase generator is how each configuration produces power. Typically, a single-phase is fitted with either one (1) or two (2) wires and a neutral, producing power in a single sine wave, whereas a three-phase system is fitted with three (3) wires along with a neutral, producing power in three sine waves that are 120 degrees out of phase with each other, contributing to a more constant and stable power flow.
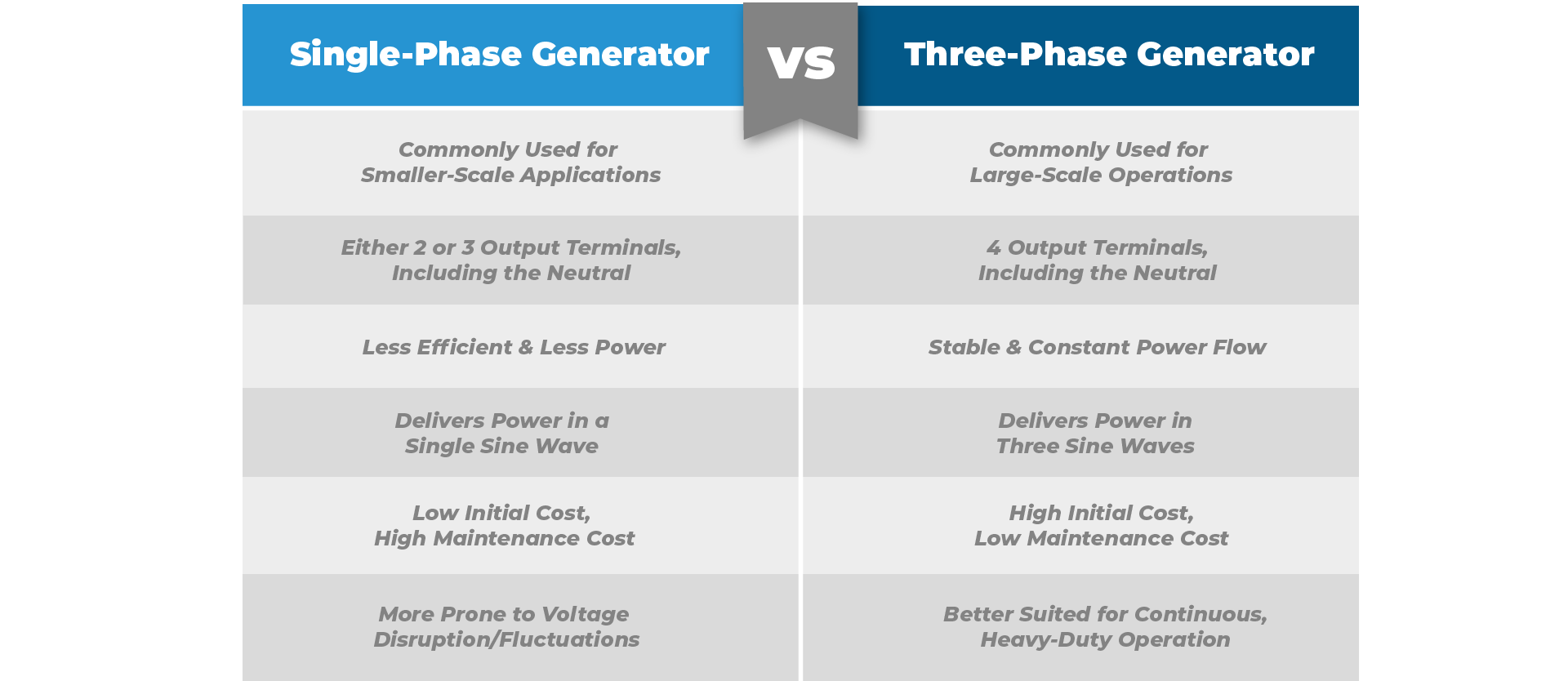
As three-phase generators provide a smoother and more reliable power delivery, they are crucial in powering sensitive loads such as industrial motors. Now, let us break down the differences between these two configurations:
Can I Power a Single-Phase Generator on a Three-Phase Load or Vice Versa?
Operating a single-phase generator with a three-phase load, or vice versa, can lead to unbalanced load distribution and overloading. This occurs when the electrical load is not evenly distributed across all phases in a three-phase configuration or between the two phases in a single-phase configuration. An unbalanced load typically results from mismatched equipment, incorrect phase connections, or uneven load distribution, causing an unequal distribution of electrical load.
This can cause overheating in your generator, significantly damaging the machine parts and internal components such as the alternator, bearings, radiator core, and exhaust valve. Such damage can lead to extensive repairs or even make the generator irreparable.
Maintaining your generator’s longevity and durability can be best achieved by matching a single-phase generator with a single-phase load, similar to a three-phase generator with a three-phase load. Though not advisable, you can still apply opposing configurations to loads with minimized wear and tear. Please find out more through our Common Misconception: Generator Application Mismatch video.
Which Configuration Should You Choose?
When it comes to choosing between a single-phase or a three-phase generator, there are several factors that you need to consider, which are the application, load requirements, efficiency, and cost.
Take a look below:
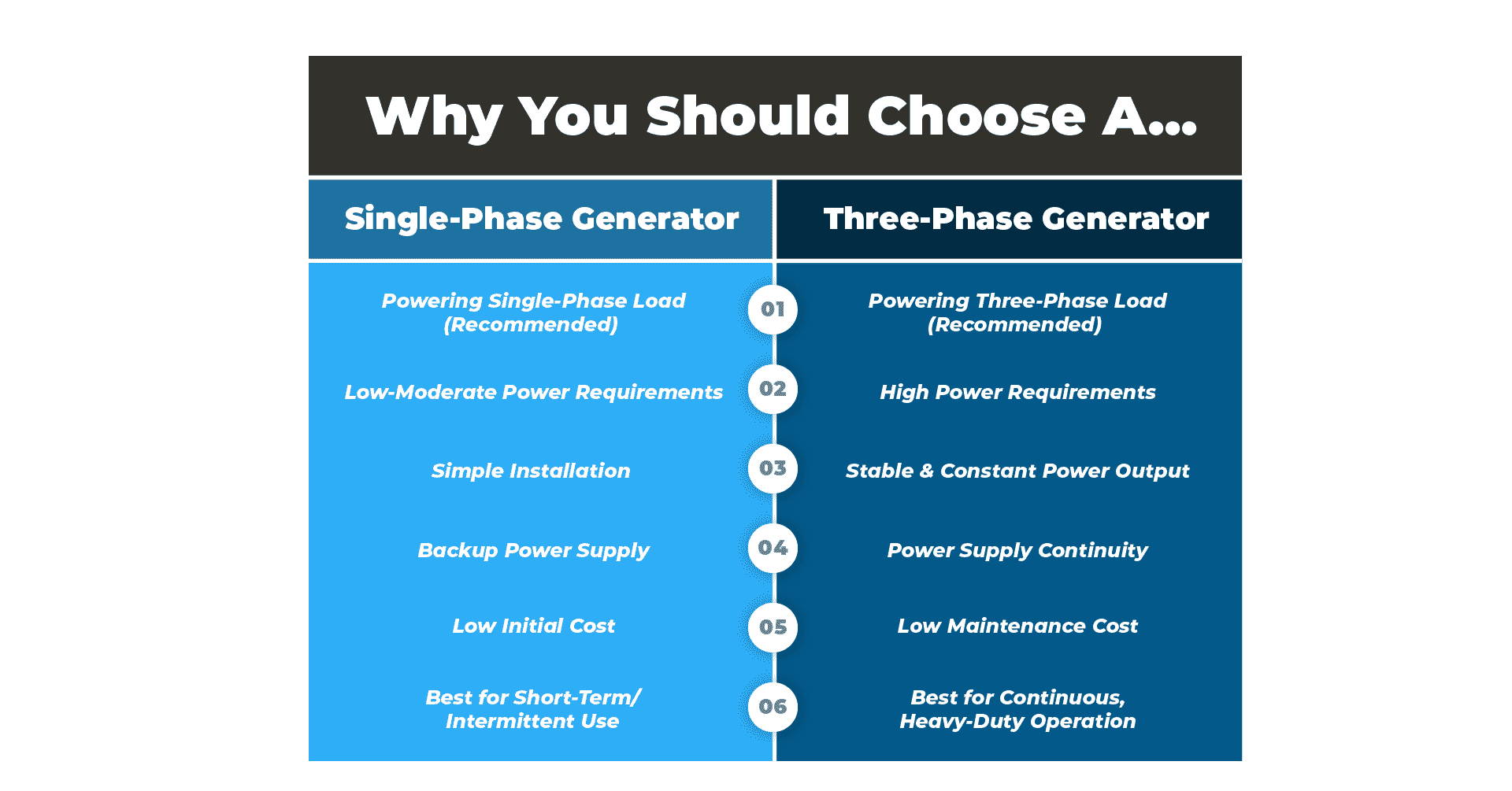
In summary, you should choose a single-phase generator when your intended use is for residential, small commercial, and light power requirements. On the contrary, three-phase generators are typically for industrial, commercial, and large-scale power requirements where efficiency and power continuity are crucial.
Conclusion
Selecting the right power generator for your operation can be tricky. It is important to consider not only your current power requirements but also your future needs. Additionally, load variables and load configuration should be taken into account before making a purchase or rental. Numerous quality vendors offer consultation services, and their service team will advise you on which type of generator is most suitable for your operations. Do not hesitate to contact them as it can save you time and minimize errors, so feel free to contact your generator vendor or click here to consult the Denyo team!


